NO.
|
TOPIC
|
SUBJECT CONTENT
|
|
1 |
Ratio, proportion, rate |
·
Demonstrate an understanding of the elementary ideas and notation of
ratio, direct and inverse proportion and common measures of rate;
·
Use scales in a practical situation;
·
Express direct and inverse variation in algebraic terms and use this
form of expression to find unknown quantities. |
|
2 |
Graphs of functions |
·
Construct tables of values and draw graphs for functions of the form
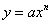 where n = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and simple
sums of not more then three of these and for functions of the form where n = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and simple
sums of not more then three of these and for functions of the form
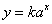 where a is a positive integer; where a is a positive integer;
·
Interpret graphs of linear, quadratic, reciprocal and exponential
functions;
·
Find the gradient of a straight line graph;
·
Solve equations approximately by graphical methods;
·
Estimate gradients of curves by drawing tangents. |
|
3 |
Coordinate geometry |
·
Demonstrate familiarity with Cartesian coordinates in two dimensions;
·
Calculate the gradient of a straight line from the coordinates of two
points on it;
·
Interpret and obtain the equation of a straight line in the form of
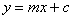 ; ;
·
Calculate the length and coordinates of the midpoint of a line segment
from the coordinates of its end points. |
|
4 |
Algebraic representation and formulae |
·
Transform simple and more complicated formulae;
·
Construct equations from given situations. |
|
5 |
Algebraic manipulation |
·
Manipulate directed numbers;
·
Use brackets and extract common factors;
·
Expand products of algebraic expressions;
·
Factorise expressions of the form
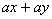 ; ; 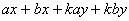 ; ; 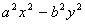 ; ; 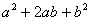 ; ; 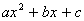 ; ;
·
Manipulate simple algebraic fractions. |
|
6 |
Indices |
·
Use and interpret positive, negative, zero and fractional indices. |
|
7 |
Solutions of equations and inequalities |
·
Solve simultaneous linear equations in two unknowns;
·
Solve quadratic equations by factorisation and either by use of the
formula or completing the square;
·
Solve simple linear inequalities. |
|
8 |
Bearings |
·
Interpret and use three-figure bearings measured clockwise from the
north (i.e. 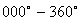 ). ). |
|
9 |
Symmetry |
·
Use the following symmetry properties of circles
(a)
Equal chords are equidistant from the centre;
(b)
The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through the centre;
(c)
Tangents from an external point are equal in length. |
|
10 |
Angle |
·
Calculate unknown angles and solve problems (including problems
leading to some notion of proof) using the following geometrical
properties:
(a)
Angle in a semi-circle;
(b)
Angle between tangent and radius of a circle;
(c)
Angle at the centre of the circle is twice the angle at the
circumference;
(d)
Angles in the same segment are equal;
(e)
Angles in opposite segments are supplementary. |
|
11 |
Trigonometry |
·
Solve trigonometrical problems in two dimensions including those
involving angles of elevation and depression and bearings;
·
Extend sine and cosine functions to angles between
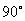 and and 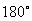 ; ;
·
Solve problems using any sine and cosine rules for any triangle and
the formula 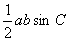 for the area of triangle; for the area of triangle;
·
Solve simple trigonometrical problems in three dimensions.
(Calculations of the angle between two planes or of the angle between
a straight line and a plane will not be required.) |
|
12 |
Statistics |
·
Collect, classify and tabulate statistical data;
·
Read, interpret and draw simple inferences from tables and statistical
diagrams;
·
Construct and use bar chars, pie charts, pictograms, dot diagrams,
stem-and-leaf diagrams, simple frequency distributions and frequency
polygons;
·
Use frequency density to construct and read histograms with equal and
unequal intervals;
·
Calculate the mean, median and mode for individual data and
distinguish between the purposes for which they are used;
·
Construct and use cumulative diagrams;
·
Estimate the median, percentiles, quartiles and interquartile range
from the cumulative frequency diagrams;
·
Calculate the mean for grouped data;
·
Identify the modal class from a group frequency distribution. |
|
|
|
|